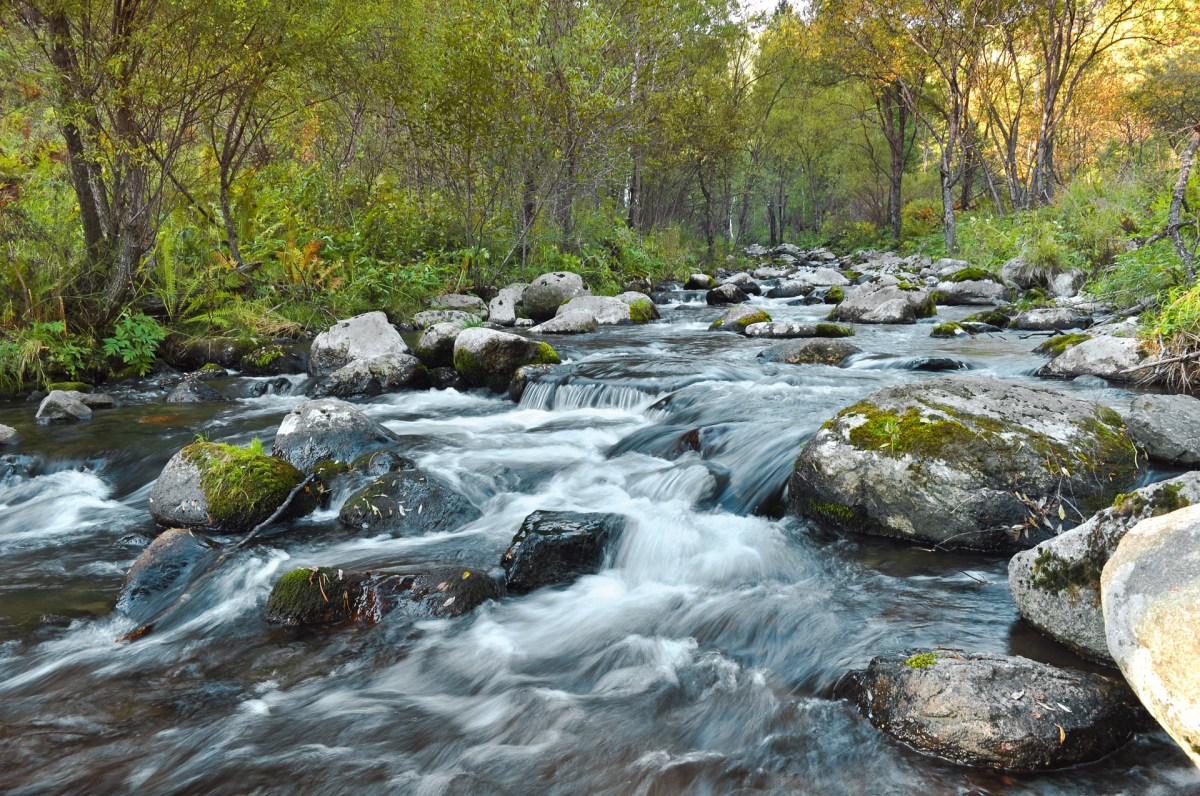
Gully meaning encompasses far more than just a ditch in the ground. It’s a term with surprisingly diverse applications, from the geological formation of deep channels carved by water erosion to its figurative use in everyday language. This exploration delves into the various facets of “gully,” revealing its scientific, environmental, and even cultural significance. We’ll examine the processes behind gully erosion, its impact on landscapes and communities, and the different ways this word finds its place in our world.
From understanding the mechanics of gully formation to exploring its metaphorical interpretations, we’ll uncover the rich tapestry of meanings associated with this seemingly simple word. We’ll also look at practical solutions for managing and mitigating the effects of gully erosion, a crucial aspect of environmental conservation and sustainable land management.
Understanding Gullies: A Comprehensive Guide
Gullies, those dramatic erosional features often seen scarring landscapes, are more than just unsightly blemishes. They represent a complex interplay of geological processes, environmental impacts, and even linguistic nuances. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of gullies, exploring their formation, impact, and various interpretations.
Defining “Gully” in Different Contexts
A gully is a channel or ditch formed by the erosional action of running water. This definition, however, can vary depending on the context. Geographically, it refers to a significant incision in the land, deeper and wider than a rill but smaller than a canyon. The formation process involves the detachment and transport of soil and rock particles by water flow, often exacerbated by factors like rainfall intensity, soil type, and vegetation cover.
Gullies can range in size from small, shallow channels to large, deeply incised features spanning hundreds of meters. Their shapes vary considerably, from V-shaped to U-shaped, depending on the erosional processes involved. The impact on the surrounding environment includes soil loss, habitat disruption, and altered water flow patterns.
| Gully Type | Formation Process | Size/Shape | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sheet erosion gully | Gradual soil removal by sheet flow | Small, shallow, often branching | Slopes with low vegetation |
| Rill gully | Concentrated flow in small channels | Small, linear, often temporary | Slopes with exposed soil |
| Headcut gully | Retreating erosion at the gully head | Steep-sided, V-shaped | Steep slopes |
| Gully with a drainage basin | Complex erosion involving runoff accumulation | Large, complex, often with tributaries | Varied topography |
Gully Erosion and its Impact

Gully erosion is a severe form of soil degradation, driven primarily by the erosive power of water. Contributing factors include intense rainfall, steep slopes, bare or sparsely vegetated land, and unsustainable land management practices. The environmental consequences are significant, including loss of fertile topsoil, reduced water quality, habitat fragmentation, and increased sediment loads in streams and rivers. Economically, gully erosion impacts agriculture through reduced crop yields and land degradation, while infrastructure damage from gully formation can be costly to repair.
- Implementing conservation tillage practices
- Planting vegetation cover to stabilize soil
- Constructing terraces and check dams
- Improving drainage systems
- Implementing sustainable land management practices
Gully as a Term in Other Fields, Gully meaning
Beyond its geographical meaning, “gully” finds application in various contexts. In some urban areas, “gully” is slang for a narrow, dark alleyway. In the context of urban planning, it might refer to a storm drain or similar drainage system. The figurative use often conveys a sense of narrowness, confinement, or obscurity, contrasting sharply with the literal, expansive image of a geographical gully.
The historical evolution of the term likely stems from its descriptive power, capturing the essence of a narrow, channeled feature across various domains.
- Geographical feature: A channel eroded by water.
- Urban slang: A narrow alleyway.
- Plumbing: A drainpipe.
- Informal: A difficult situation or predicament.
Visual Representation of Gullies
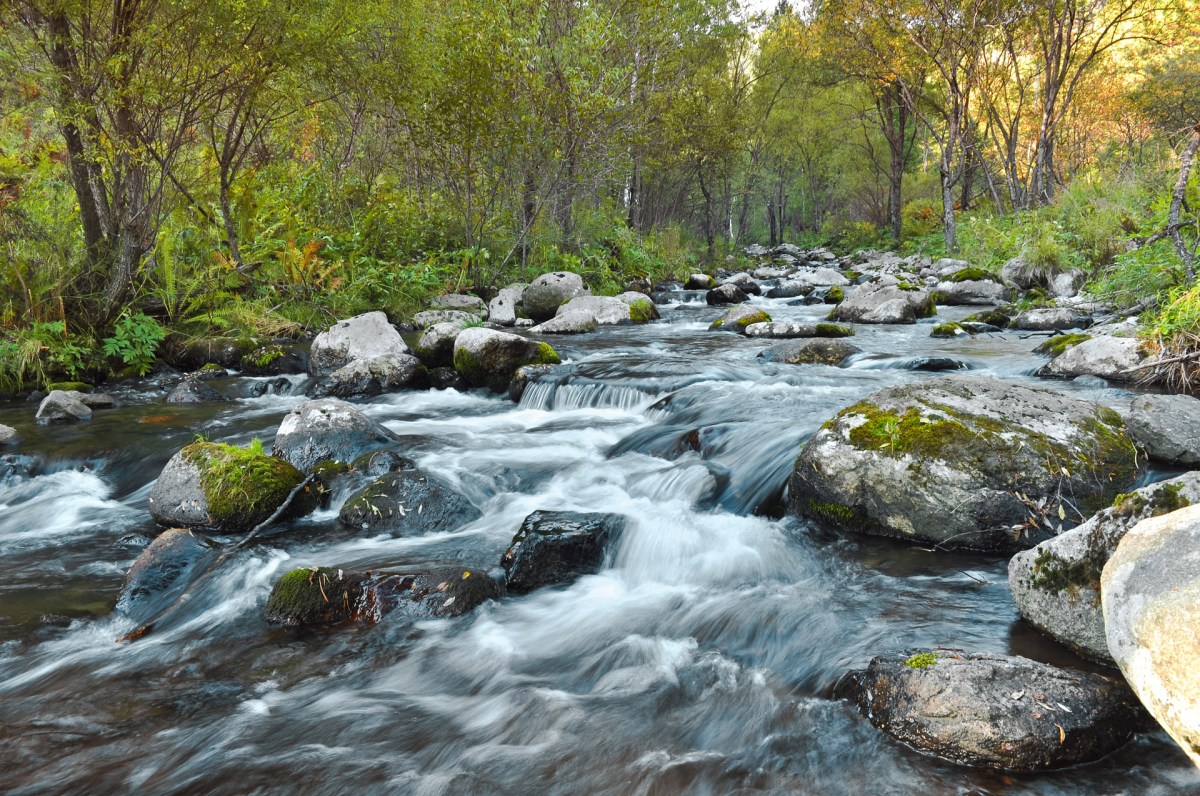

A typical gully presents a visually striking landscape feature. Its shape can range from a shallow, V-shaped channel to a deep, U-shaped incision. The color often reflects the soil composition, varying from reddish-brown in clay soils to lighter shades in sandy areas. Vegetation is typically sparse within the gully itself, although the surrounding areas may be more vegetated. Young gullies often exhibit steep sides and a relatively narrow channel, while older gullies may have gentler slopes and a wider, more established channel.
So, “gully” means a ditch or channel, right? Think of the pathways carved by rainwater. Now, imagine those pathways as the frantic escape routes in the classic centipede video game , where you’re dodging those creepy crawlies. The game’s design, with its winding paths, almost feels like a network of miniature gullies, doesn’t it? Understanding the meaning of “gully” helps visualize the game’s layout better.
The visual appearance can reveal insights into the gully’s formation and age; for example, the presence of headcuts indicates active erosion.
Imagine a landscape dominated by a large, U-shaped gully. Its steep walls are scarred with evidence of past landslides. At the bottom, a small stream flows, carrying sediment downstream. The surrounding area is characterized by sparse vegetation, with drought-resistant shrubs clinging to the slopes. The contrast between the barren gully and the greener surrounding hills accentuates the impact of erosion.
So, you’re wondering about “gully meaning”? Basically, it refers to a channel or ditch worn away by water. Think of the strategic planning involved – it’s kind of like navigating the terrain in the commanders game , where understanding the landscape is key to success. Understanding the contours of a gully, just like mastering the game’s map, helps you anticipate and plan effectively.
Ultimately, understanding gully meaning helps you grasp its impact on the surrounding environment.
Gully Management and Remediation
Gully management and remediation involve a range of techniques aimed at preventing further erosion and restoring degraded land. These methods are guided by principles of soil conservation, hydrology, and ecological restoration. Approaches include mechanical stabilization (e.g., check dams, contour bunds), biological stabilization (e.g., vegetation planting, bioengineering), and hydrological management (e.g., improved drainage, water harvesting). The choice of technique depends on factors such as gully size, slope, soil type, and available resources.
End of Discussion: Gully Meaning
Understanding “gully meaning” requires a multidisciplinary approach, bridging geology, environmental science, and even linguistics. Whether you’re a geologist studying land formations, an environmentalist concerned with erosion, or simply curious about the word’s diverse usage, this exploration has hopefully illuminated the multifaceted nature of “gully.” From its literal definition to its figurative applications, the term holds a significant place in our understanding of the natural world and human language.
General Inquiries
What is the difference between a gully and a ravine?
So, you’re wondering about “gully meaning”? It usually refers to a small, narrow ravine, right? But did you know that the term can also be used figuratively? Think about the chaotic energy of a khabib plane – a bit of a wild ride, maybe even a bit of a “gully” of a situation. Understanding the context helps clarify the intended meaning of “gully,” whether it’s a geographical feature or a metaphor for something turbulent.
While both are erosional features, ravines are generally larger and deeper than gullies. Gullies are typically smaller and can often be found as part of a larger ravine system.
Can gullies be repaired or restored?
Yes, gully remediation is possible through various techniques like terracing, check dams, and revegetation, depending on the size and severity of the gully.
What are some slang uses of the word “gully”?
In some dialects, “gully” can be slang for a street or alleyway, particularly in urban settings.
How does climate change affect gully erosion?
Increased intensity and frequency of rainfall events associated with climate change can exacerbate gully erosion.
