How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate data collection. Mastering drone operation requires understanding its mechanics, navigating regulations, and honing piloting skills. This guide delves into each aspect, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to safely and effectively pilot your drone.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and basic flight controls to advanced techniques like waypoint navigation and capturing stunning aerial imagery. We’ll also explore essential safety procedures, legal considerations, and effective post-processing workflows. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will serve as your trusted companion on your drone journey.
Drone Components and Their Functions
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section details the function of key components and explores the variations within those components.
Drone Propeller Types and Their Impact on Flight
Drone propellers come in various designs, each affecting flight characteristics. Common propeller types include those with a high pitch for increased thrust and speed, and those with a low pitch for improved efficiency and longer flight times. The number of blades also influences performance; two-bladed propellers are generally lighter and faster, while multi-bladed propellers offer more stability and lift at lower speeds.
Propeller size is another critical factor; larger propellers generate more thrust, while smaller propellers are more efficient. The material of the propeller, such as carbon fiber or nylon, also impacts its durability and weight.
Major Drone Components
The major components of a drone and their functions are detailed below.
- Propellers: Generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, fly, and maneuver.
- Motors: Power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, responsible for processing sensor data and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands.
- Battery: Provides power to all drone components. Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Different drones feature cameras with varying resolutions, sensors, and features.
- GPS: Allows the drone to determine its location, enabling features like autonomous flight and Return-to-Home (RTH).
Comparison of Three Drone Models
| Feature | Drone Model A | Drone Model B | Drone Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Flight Time | 25 minutes | 30 minutes | 20 minutes |
| Max Speed | 60 km/h | 50 km/h | 70 km/h |
| Weight | 750g | 850g | 600g |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
Thorough pre-flight checks are essential for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents or equipment damage. This section provides a comprehensive checklist and illustrates the pre-flight sequence.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
- Inspect the drone’s body for any damage or loose parts.
- Check the propellers for damage or wear.
- Ensure the battery is fully charged and securely connected.
- Verify that the GPS signal is strong and stable.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Test the motors and propellers for proper function.
- Review the flight plan and ensure it is safe and legal.
- Check weather conditions and avoid flying in adverse weather.
Battery Calibration and Charging
Proper battery calibration and charging are critical for optimal performance and longevity. Calibration ensures accurate battery level readings, preventing unexpected power failures mid-flight. Charging should always be done using the manufacturer’s recommended charger and procedures to avoid overcharging or damaging the battery. Never leave LiPo batteries unattended while charging.
Pre-Flight Sequence Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight sequence would enhance understanding. The flowchart would start with power-on self-tests, progress to visual inspection, then GPS acquisition, and finally motor calibration checks before proceeding to the flight.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to operating a drone safely and effectively. This section covers the function of control sticks, essential maneuvers, and techniques for stable flight in various conditions.
Drone Controller Functions
Most drone controllers utilize two joysticks. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward movement) and roll (left/right movement).
Takeoff, Landing, Hovering, and Directional Movements
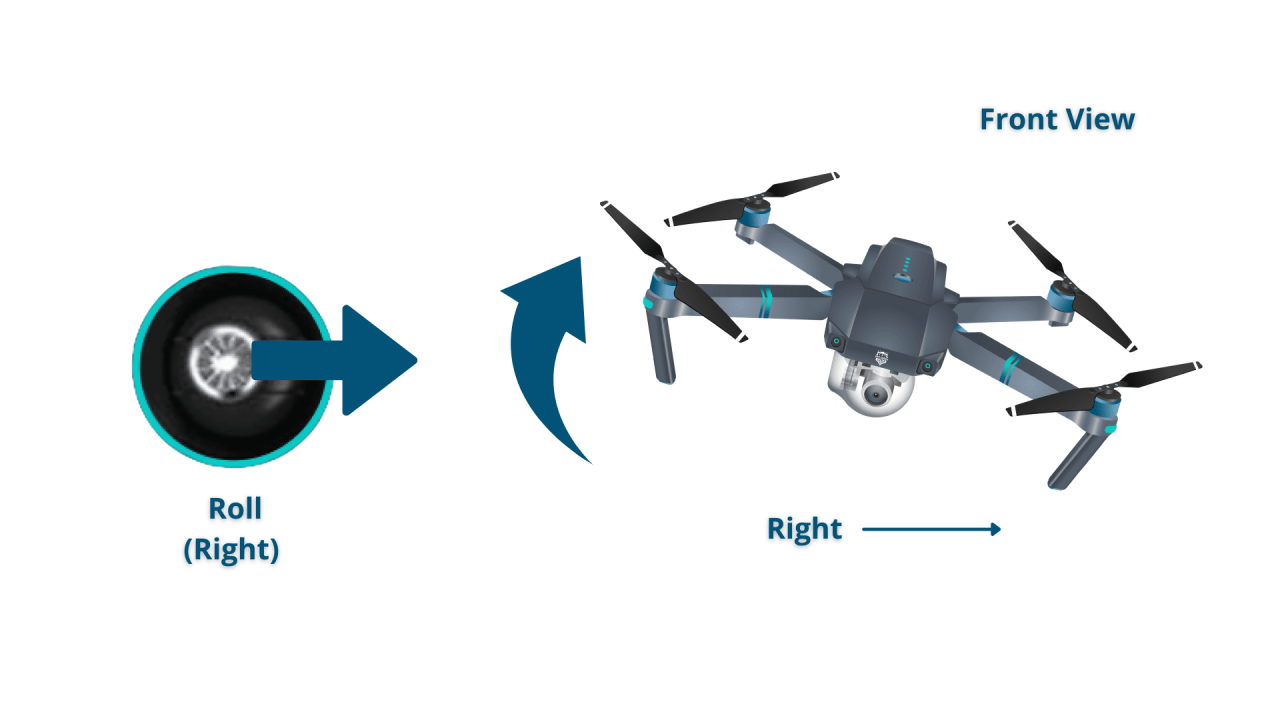
Takeoff involves gently increasing throttle until the drone lifts off vertically. Landing is the reverse, gradually decreasing throttle until the drone gently touches down. Hovering requires maintaining a stable position in the air by carefully adjusting the control sticks. Directional movements are achieved by using the right joystick to control pitch and roll, moving the drone forward, backward, left, or right.
Maintaining Stable Flight in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires more skill and awareness. It is advisable to reduce speed and maintain a steady throttle. Adjusting the control sticks smoothly and anticipating wind gusts are crucial for maintaining stability.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques enable more complex and efficient drone operations. This section explores waypoint navigation, challenges in complex environments, and strategies for emergency situations.
Waypoint Navigation and Mission Planning
Waypoint navigation involves programming a series of points for the drone to follow autonomously. Mission planning software allows users to create detailed flight plans, including waypoints, altitude, speed, and camera settings. This is particularly useful for aerial photography and surveying.
Challenges of Flying in Complex Environments
Urban areas present challenges such as obstacles (buildings, trees, power lines), radio interference, and restricted airspace. Forests pose challenges due to signal loss from dense foliage and the risk of collisions with trees. Careful planning and risk assessment are vital when operating in these environments.
Emergency Situation Strategies, How to operate a drone
- Loss of Signal: Most drones have a Return-to-Home (RTH) function, which automatically guides the drone back to its starting point.
- Low Battery: Immediately initiate RTH or carefully land the drone in a safe location.
- Unexpected Malfunction: Attempt a controlled landing. If unsuccessful, prepare for a potential crash and prioritize safety.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding camera settings and techniques is key to capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section explains camera settings and provides a step-by-step guide for capturing compelling visuals.
Camera Settings: Aperture, Shutter Speed, ISO
Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera lens. A wider aperture (lower f-number) lets in more light, useful in low-light conditions, but can reduce depth of field. A narrower aperture (higher f-number) increases depth of field, keeping more of the scene in focus.
Shutter Speed: Controls how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower shutter speeds can create motion blur. It also affects the amount of light captured.
ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are needed in low-light conditions but can introduce noise (grain) into the image.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
- Choose the right camera settings based on lighting conditions and desired effect.
- Plan your shots carefully, considering composition and perspective.
- Fly smoothly and avoid jerky movements to prevent blurry images.
- Use appropriate filters (ND filters for reducing light in bright conditions).
- Post-process your images to enhance color, contrast, and sharpness.
Comparison of Drone Camera Features
| Feature | Camera A | Camera B | Camera C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Size | 1/2.3″ | 1/1.7″ | 1″ |
| Resolution | 4K | 4K | 6K |
| Aperture Range | f/2.8 | f/2.0 | f/2.8 – f/11 |
| Features | HDR, Electronic Image Stabilization | HDR, 3-axis Gimbal | HDR, 3-axis Gimbal, RAW Capture |
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for keeping your drone in optimal condition. This section provides a maintenance schedule and guidance on resolving common issues.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule should include inspecting propellers for damage, cleaning the drone body, checking for loose screws, and ensuring proper battery care. The frequency of these checks depends on the drone’s usage, but a monthly inspection is generally recommended.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Common issues include motor failures (check for loose connections or damaged motors), GPS signal loss (check for obstructions or interference), and battery problems (ensure proper charging and storage). Always refer to the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide for specific solutions.
Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
- Check the controller’s batteries.
- Ensure the drone and controller are properly paired.
- Restart both the drone and controller.
- Check for interference from other electronic devices.
- Update the drone’s firmware.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Operating a drone legally requires understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This section highlights the importance of legal compliance and responsible flying.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone laws vary by region and country. These laws often cover registration requirements, flight restrictions (e.g., near airports or sensitive areas), and operational limits (e.g., maximum altitude and distance). It is crucial to research and comply with all applicable regulations before operating a drone.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which offers comprehensive guidance. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation, maximizing your aerial experience.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones

Many areas are designated as restricted airspace, such as airports, military bases, and national parks. Flying in these zones can result in fines or legal repercussions. It’s important to use a flight planning app that identifies these restricted zones.
Obtaining Necessary Permits and Licenses
Depending on the type of drone operation and location, permits or licenses may be required. Commercial drone operations usually require specific certifications and licenses. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Safety Procedures and Best Practices
Safe drone operation is paramount. This section emphasizes responsible flying practices and procedures for handling unexpected situations.
Importance of Safe Drone Operation and Responsible Flying
Safe drone operation involves careful planning, pre-flight checks, and adherence to all laws and regulations. Responsible flying considers the safety of others and the environment. Always maintain visual contact with the drone, avoid flying near people or property, and be mindful of wildlife.
Safety Tips to Prevent Accidents
- Never fly beyond your visual line of sight.
- Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Always check battery levels before and during flight.
- Be aware of your surroundings and potential hazards.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
Handling Unexpected Situations
In case of near misses or malfunctions, prioritize safety. Attempt a controlled landing, and if unable, prepare for a potential crash. Report any incidents to the relevant authorities.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
This section explores the principles of aerial photography and videography, focusing on capturing compelling visuals from unique perspectives.
Principles of Aerial Photography and Videography Composition
Aerial photography and videography leverage unique perspectives to create visually striking images. Key compositional elements include the rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry. Understanding light and shadow is also crucial for creating impactful visuals.
Capturing Compelling Visuals from Unique Perspectives
Aerial perspectives offer unparalleled opportunities for creative storytelling. Consider shooting from different angles and heights to highlight the subject and surrounding environment. Experiment with different compositions and perspectives to discover unique and compelling visuals.
Techniques for Achieving Cinematic Shots
Cinematic shots involve using smooth movements and transitions to create a visually engaging experience. Techniques such as slow pans, reveals, and dynamic tracking shots enhance the storytelling capabilities of aerial footage.
Post-Processing and Editing

Post-processing and editing are crucial for enhancing the quality and storytelling potential of drone footage. This section introduces the basics of post-processing and provides resources for advanced learning.
Basics of Post-Processing Drone Footage
Post-processing involves adjusting various aspects of the image or video, such as color correction, contrast enhancement, and sharpening. Software such as Adobe Lightroom and Photoshop are commonly used for photo editing, while Adobe Premiere Pro and DaVinci Resolve are popular for video editing.
Using Editing Software to Enhance Image Quality
Editing software allows for more advanced adjustments and creative control. Techniques such as color grading, adding effects, and stabilizing footage can significantly enhance the overall quality and impact of the visuals.
Resources for Learning Advanced Editing Techniques
Numerous online resources are available for learning advanced editing techniques. Online tutorials, courses, and communities provide valuable learning opportunities for improving drone footage post-processing and editing skills.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical understanding, practical skills, and responsible decision-making. From understanding the intricacies of your drone’s components to adhering to safety regulations and mastering flight techniques, each step contributes to a safe and rewarding experience. By combining theoretical knowledge with practical application, you can unlock the full potential of your drone and capture breathtaking aerial perspectives.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a fantastic resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from controls to safety procedures. Ultimately, safe and responsible drone operation requires consistent practice and a thorough understanding of the technology.
Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
FAQ Summary
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Research models known for ease of use and consider your budget.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is recommended, especially if you’ve transported it or experienced significant magnetic interference. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
What should I do if I lose signal with my drone?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If the RTH fails, attempt to regain signal by moving to a higher vantage point with a clearer line of sight.
How do I ensure my drone footage is legally compliant?
Always check local and national regulations regarding drone operation. This includes airspace restrictions, required permits, and privacy laws. Fly responsibly and respect others’ privacy.
